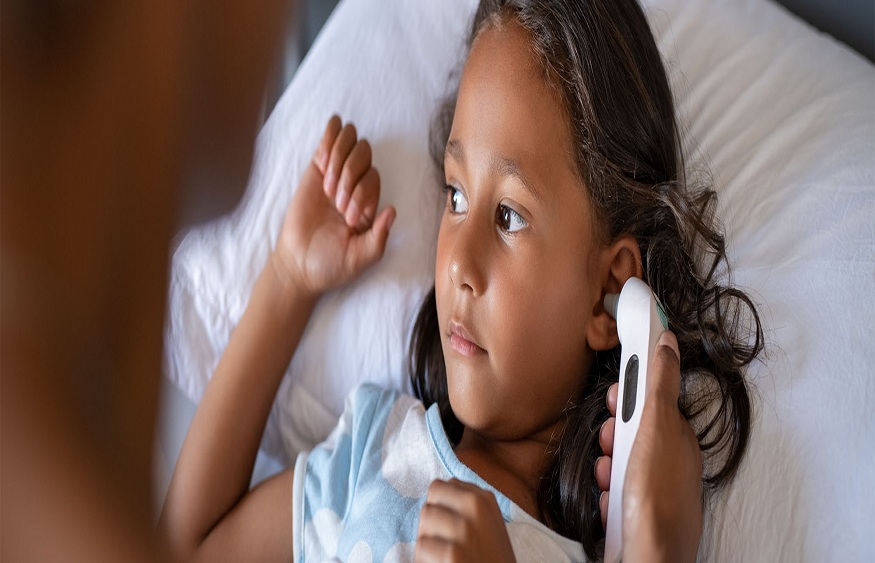
Ear infections are a common condition, especially among children, characterized by inflammation and infection in the middle ear. They can cause significant discomfort, pain, and temporary hearing loss. Effective ear treatment is crucial to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial ear infections, but there are also other treatment options available. In this blog post, we will explore the role of antibiotics and other treatments in the management of ear infections.
Understanding Ear Infections
There are three main types of ear infections:
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM): This is the most common type of ear infection, typically occurring due to a bacterial or viral infection. It causes rapid onset of symptoms, including ear pain, fever, and sometimes fluid drainage from the ear.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): OME refers to the presence of fluid in the middle ear without active infection. It can occur after an acute infection has resolved or due to other factors like allergies or Eustachian tube dysfunction. OME may not always require immediate treatment.
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM): CSOM is a persistent infection of the middle ear, characterized by long-lasting drainage of fluid or pus from the ear. It often requires specialized treatment and management.
Role of Antibiotics
- Bacterial Infections: Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial ear infections to target and eliminate the infection-causing bacteria. Commonly used antibiotics for ear infections include amoxicillin, cefdinir, and azithromycin. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
- Viral Infections: Many ear infections are viral in nature, and antibiotics are ineffective against viruses. In these cases, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and allowing the infection to resolve on its own. Overusing antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance, so they should be used judiciously.
Other Treatment Options
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate ear pain and reduce fever associated with ear infections. Follow the recommended dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if the pain persists or worsens.
- Ear Drops: Depending on the type and severity of the ear infection, a healthcare professional may recommend antibiotic ear drops to deliver medication directly to the affected area. Ear drops can be especially useful for infections that do not require systemic antibiotics.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Ensure the compress is warm, not hot, and place it gently against the outer ear.
- Observation and Supportive Care: In some cases, especially with mild ear infections or OME, healthcare professionals may recommend observation and supportive care. This may involve regular follow-up visits to monitor the infection’s progress and ensure appropriate treatment if needed.
Prevention Tips
Preventing ear infections is not always possible, but the following measures may help reduce the risk:
– Maintain good hand hygiene and teach children proper handwashing techniques.
– Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke, which can increase the risk of ear infections.
– Keep up to date with vaccinations, including the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and influenza vaccine.
– Promptly treat respiratory infections to minimize the risk of secondary ear infections.
Ear infections can cause significant discomfort, particularly in children, but appropriate treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Antibiotics play a crucial role in treating bacterial ear infections, while supportive care and other treatments can help manage symptoms and promote comfort. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. With proper care, most ear infections can be effectively treated, allowing individuals to recover and resume their daily activities.